-
User guide
- Part 1 - Introduction
- Part 2 - Core Restlet
- Part 3 - Restlet Editions
- Part 4 - Restlet Extensions
- Appendices
- Tutorials
- Javadocs
- Change Log
Overview
Introduction
The org.restlet.resource package contains client and server resource classes.
Architecture
Below is an overview of the architecture, including all processing layers, from the lowest TCP/IP network layer to the highest annotated interface proxies.
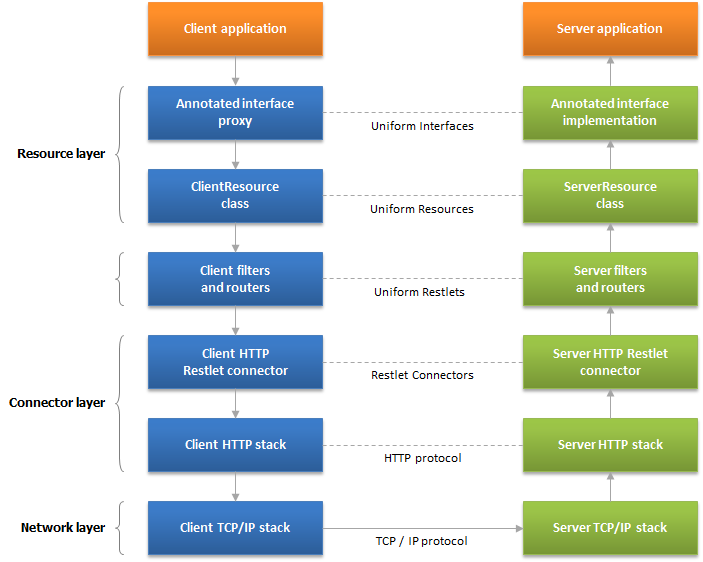
Class diagram
Here is a class diagram:
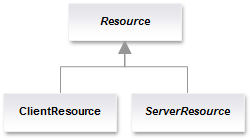
Annotations
We also defined a set of method level annotations:
| Annotation | Description |
|---|---|
| @Delete | Annotate methods that remove resources. |
| @Get | Annotate methods that represent a variant of a resource |
| @Options | Annotate methods that accept representations. |
| @Post | Annotate methods that accept representations. |
| @Put | Annotate methods that store representations. |
Those annotations are specific to the Restlet API and shouldn’t be confused with those of the JAX-RS API. For support of the JAX-RS API by the Restlet Framework, you should look at the provided extension.
Annotations parameter
All annotation have a single optional parameter. Its name is the default “value” name allowing a compact annotation syntax.
Here is the grammar for this parameter:
CHARACTER = 'a-z' | 'A-Z' | '0-9'
TOKEN = CHARACTER [CHARACTER]*
EXTENSION = TOKEN
PARAMETER = TOKEN ['=' TOKEN]
VARIANT = EXTENSION ['+' EXTENSION]*
ENTITY = VARIANT ['|' VARIANT]*
INPUT = ENTITY
OUTPUT = ENTITY
QUERY = PARAMETER ['&' PARAMETER]
ANNOTATION = INPUT [',' INPUT]* [':' OUTPUT] ['?' QUERY]
Here are some valid values:
// Returns a representation in the "text/xml" media type
@Get("xml")
String toString();
// Stores representations in the "text/xml" media type
// after conversion to a DOM document
@Put("xml")
void store(Document doc)
// Stores representations in the "text/xml" media type after
// conversion to a DOM document and returns a plain text response
@Put("xml:txt")
String store(Document doc)
// Returns a representation in the "text/xml" media type with
// an inlining depth level of 2
@Get("xml?depth=2")
// Alternative variants
@Put("xml|json:json")
// Alternative variants
@Put("xml+ascii | json+utf8 : json")
Note the importance of registering the proper extension names via the MetadataService in order to use additional extension names.
Sample code
Here is how a sample resource would look like with the refactored API. Note that both extension names and full MIME type would be supported. Extensions can be updated via the MetadataService.
import java.io.InputStream;
import org.restlet.ext.atom.Feed;
import org.restlet.resource.Delete;
import org.restlet.resource.Get;
import org.restlet.resource.Post;
import org.restlet.resource.Put;
import org.restlet.resource.Representation;
import org.restlet.resource.ServerResource;
import org.w3c.dom.Document;
public class TestResource extends ServerResource {
@Get
public Feed toAtom() {
// ...
return null;
}
@Get("xml?deep")
public Representation toXml() {
// ...
return null;
}
@Post("xml:xml")
public Representation accept(Document entity) {
// ...
return null;
}
@Put("atom|json")
public void storeAtom(Feed feed) {
// ...
}
@Put("cust")
public void storeXml(InputStream stream) {
// ...
}
@Delete
public void removeAll() {
// ...
}
}
